Optical Emission Spectrometer
Optical Emission Spectroscopy Definition
The photoelectric optical emission spectrometry refers to the emission spectroscopy that uses the photoelectric conversion receiving method for simultaneous analysis of multiple elements. Due to the widespread use of inductively coupled high-frequency plasma light sources, the photoelectric optical spectroscopy occupies a major position in the spectrometer.
Optical Emission Spectroscopy Working Principle
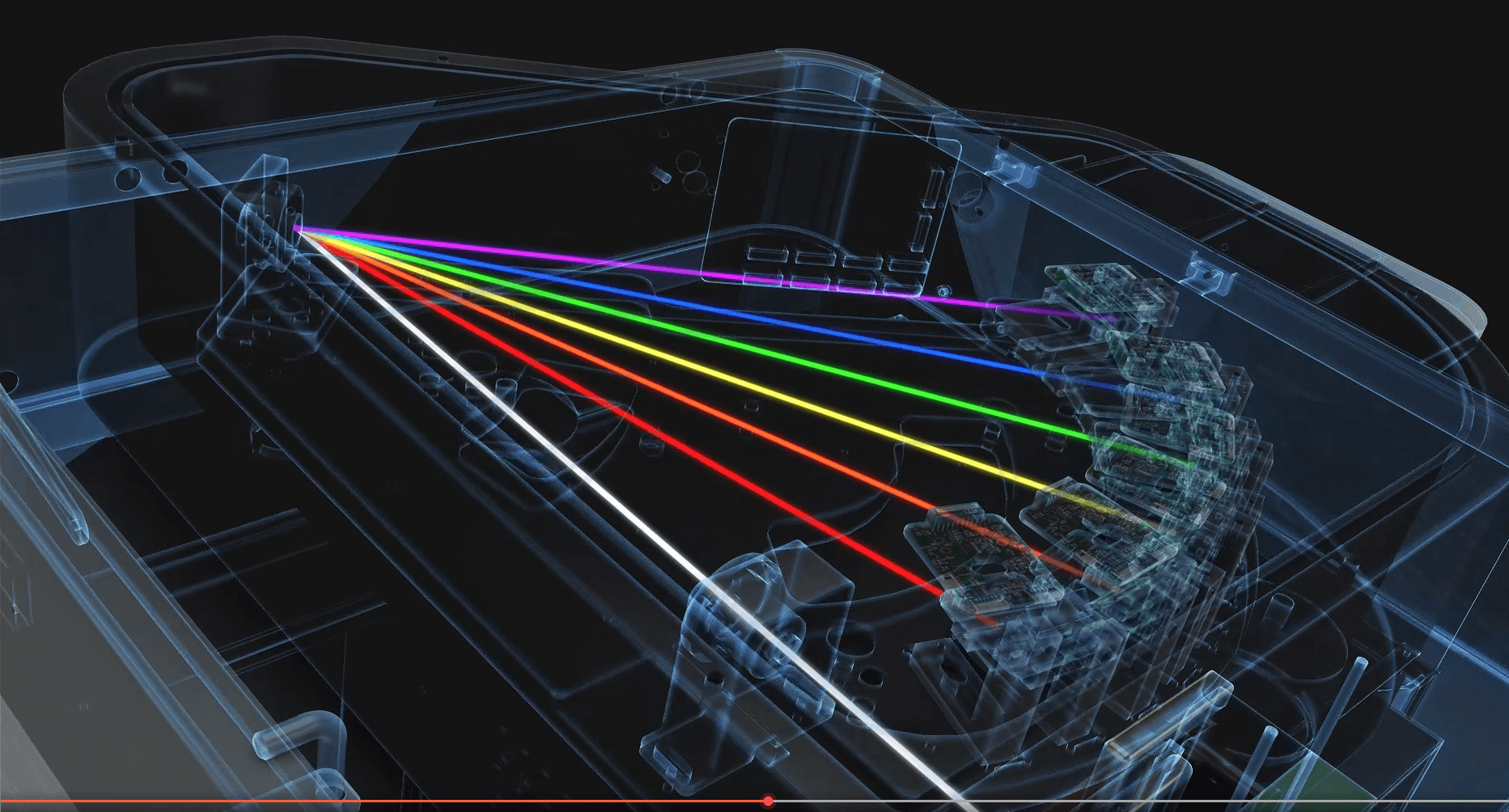
The working principle of the photoelectric optical emission spectrometer is that the sample is excited by an electric arc or spark discharge to generate atomic vapor, and the neat atoms and the sample are excited to produce an emission spectrum. The emission spectrum enters the spectroscopic chamber of the spectrometer by walking around the fiber and disperses into various spectral bands. According to the different emission wavelength range of each element, the best spectral line of each element can be measured by the detector. The intensity of the emission spectrum of each element is proportional to the content of the element in the sample. The content of the instrument can be measured through the internal pre-stored calibration curve and displayed directly as a percentage concentration. This is the principle of the optical emission spectrometer.